以更优雅的方式获取 DEM 数据
DEM 数字高程模型数据是一个很常见的表现海拔高度的数据,在 GIS 和气象领域经常会用到。但是对于大部分人来说,使用 DEM 数据并不是一件简单的事情,通常情况下网上的 DEM 数据都是通过分区块的文件方式(通常文件还会被压缩)供用户下载,用户下载之后还需要专门的工具在本地进行一系列的操作才能使用,对于一些轻量使用的用户来说相当的不方便(比如我只是想画一个海南拉鲁:「用 Python 绘制你自己的海(nan)拉鲁」)。
对于大部分比较懒的用户(比如我)来说,处理拼接的过程过于枯燥和繁琐。于是我写了一个 Python 包 —— pyterrain 来解决这个痛点,下面我就来介绍一下用 pyterrain 获取 DEM 到底有多方便。
首先我们当然是需要安装它: pip install pyterrain。由于 pyterrain 自己本身并不生产 DEM 数据,它只是一个下载和处理文件的包,所以我们还需要到 https://developers.nextzen.org/ 这个网站上申请一个 api_key,这个 api_key 的申请是完全免费的,并且没有任何门槛,使用 Github 账号直接就可以登录。
申请完之后,我们只需要下面这短短的几行代码,就能根据指定的坐标范围获取DEM 的数据及其相应的坐标矩阵:
from pyterrain import Terrain
BBOX = 103.660531, 30.982824, 104.690779, 30.234884 # 成都的经纬度范围坐标:(左,上,右,下)
API_KEY = 'Dto0r88DQuaQizoxcQScvw'
terrain = Terrain(API_KEY)
lons, lats, dem = terrain.fetch(bbox=BBOX, quiet=False, coord="lonlat")
它会提示一段进度条和一些信息,然后经纬度网格和 DEM 数据就直接可以用了,是不是很方便?
如果你觉得数据的空间分辨率不够精细,可以通过在调用 fetch 方法时设置 zoom 参数来调整,zoom 实际上就是瓦片金字塔结构的缩放级别,zoom 参数越大,空间分辨率就越高,下载的文件数据量也就越大。
如果你不设置 zoom 的值,那么程序会自己寻找一个合适的缩放级别,对于只是想做一些地形可视化的用户来说这就让工作变得简单很多。
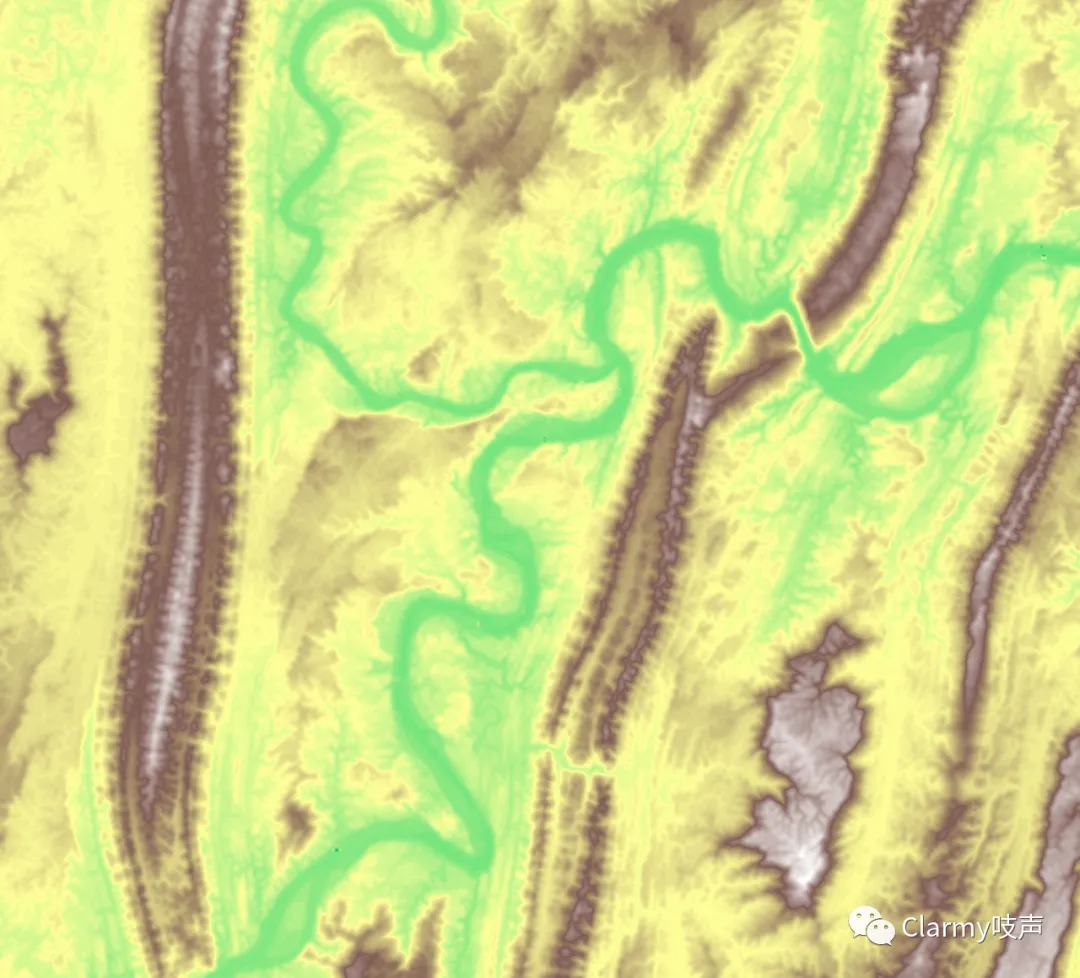
下面我们来执行一个例子,用 pyterrain 下载并绘制重庆市区的地形:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
from pyterrain import Terrain
def truncate_colormap(cmap, min_val=0.0, max_val=1.0, num_colors=100):
"""
Truncate a colormap by creating a new one from a subset of an existing.
Args:
cmap (Colormap): The original colormap.
min_val (float): The start boundary (0-1), default to 0.0.
max_val (float): The end boundary (0-1), default to 1.0.
num_colors (int): The number of colors in the new colormap. Default to 100.
Returns:
new_cmap (Colormap): The new colormap.
"""
new_cmap = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list(
"trunc({n},{a:.2f},{b:.2f})".format(n=cmap.name, a=min_val, b=max_val),
cmap(np.linspace(min_val, max_val, num_colors)),
)
return new_cmap
API_KEY = "Dto0r88DQuaQizoxcQScvw"
bbox = (106.327321, 29.704862, 106.778055, 29.347852)
cmap = truncate_colormap(plt.get_cmap("terrain"), 0.2, 1, 100)
terrain = Terrain(API_KEY)
xs, ys, elevation = terrain.fetch(bbox=bbox, quiet=False, coord="lonlat")
shape = np.array(elevation.shape)
norm = mcolors.Normalize(vmin=1, vmax=elevation.max())
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=shape[::-1] / 100, dpi=300)
contour = ax.contourf(
xs,
ys,
elevation,
cmap=cmap,
levels=100,
norm=norm,
)
ax.axis("off")
plt.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("./重庆地形.png", bbox_inches="tight", pad_inches=0, dpi=300)
来看一下效果: